cfDNA片段组学服务:液体活检前沿研究解决方案

参考文献
[1] Wan JCM, Massie C, Garcia-Corbacho J, et al. Liquid biopsies come of age: towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(4):223-238. doi:10.1038/nrc.2017.7
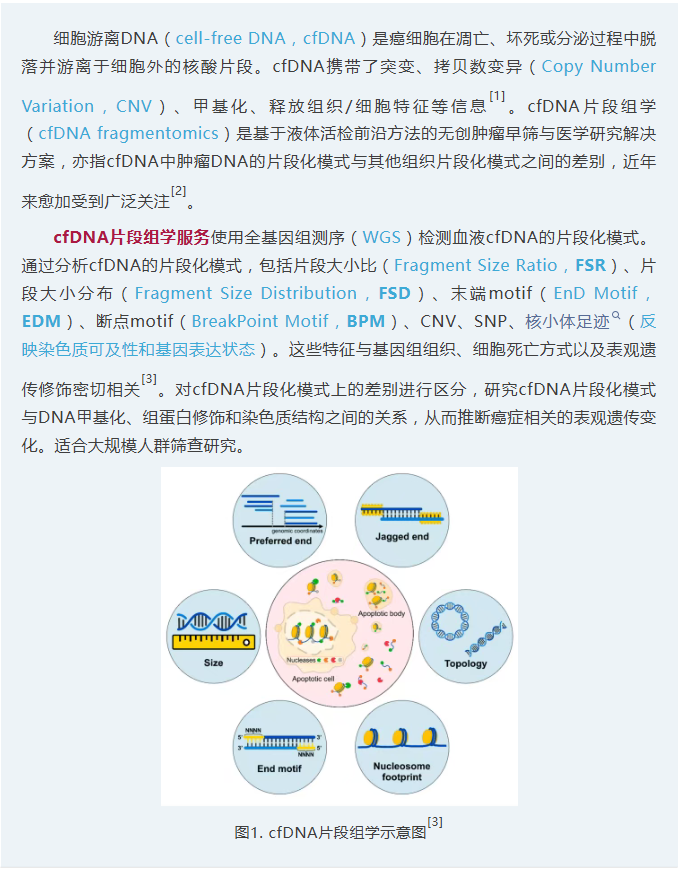
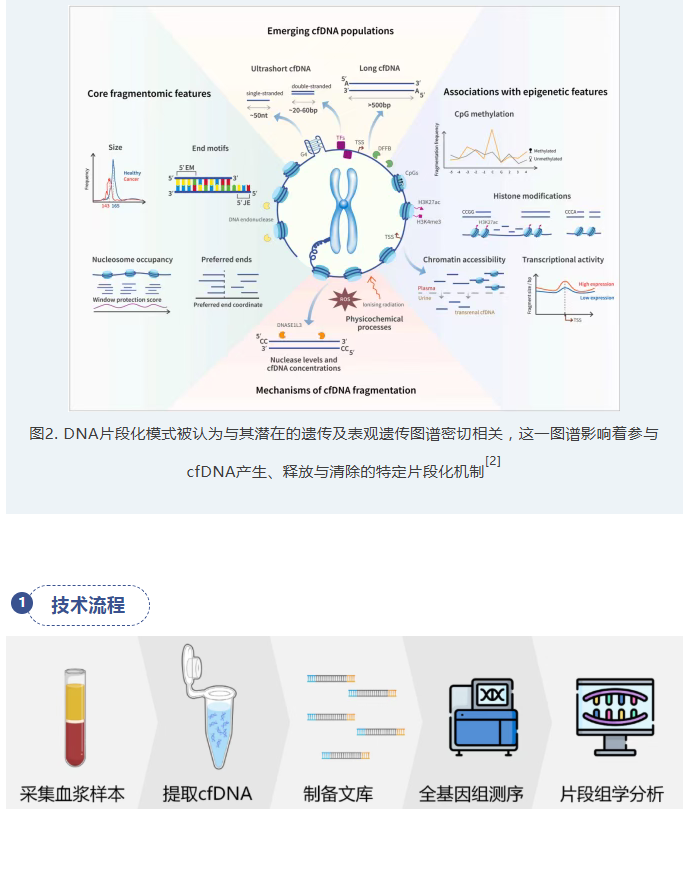
[2] Tsui WHA, Jiang P, Lo YMD. Cell-free DNA fragmentomics in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2025;43(10):1792-1814. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2025.09.006
[3] Ding SC, Lo YMD. Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomics in Liquid Biopsy. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(4):978. Published 2022 Apr 13. doi:10.3390/diagnostics12040978
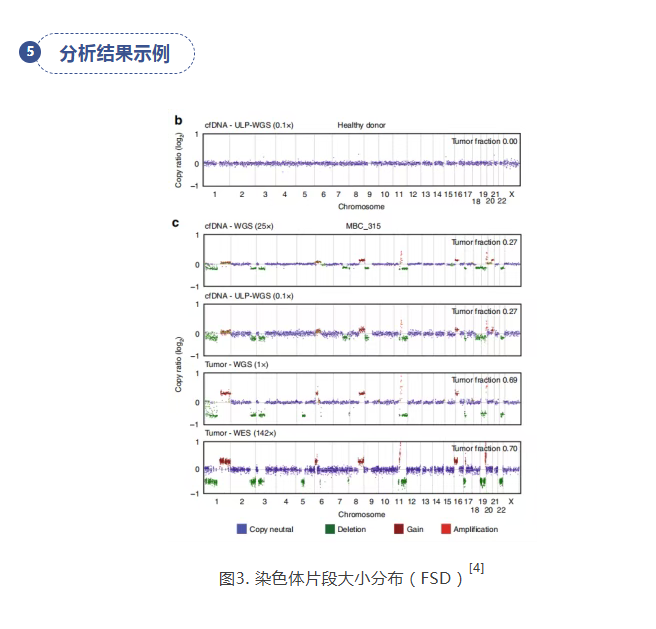
[4] Adalsteinsson VA, Ha G, Freeman SS, et al. Scalable whole-exome sequencing of cell-free DNA reveals high concordance with metastatic tumors. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1324. Published 2017 Nov 6. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00965-y
[5] Cristiano S, Leal A, Phallen J, et al. Genome-wide cell-free DNA fragmentation in patients with cancer. Nature. 2019;570(7761):385-389. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1272-6
[6] Sun K, Jiang P, Cheng SH, et al. Orientation-aware plasma cell-free DNA fragmentation analysis in open chromatin regions informs tissue of origin. Genome Res. 2019;29(3):418-427. doi:10.1101/gr.242719.118
[7] Wang S, Meng F, Li M, et al. Multidimensional Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomic Assay for Detection of Early-Stage Lung Cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207(9):1203-1213. doi:10.1164/rccm.202109-2019OC
[8] Yin L, Cao C, Lin J, et al. Development and Validation of a Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomics-Based Model for Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2025;43(26):2863-2874. doi:10.1200/JCO.24.00287
[9] Bao H, Yang S, Chen X, et al. Early detection of multiple cancer types using multidimensional cell-free DNA fragmentomics. Nat Med. 2025;31(8):2737-2745. doi:10.1038/s41591-025-03735-2
[10] Bai J, Jiang P, Ji L, et al. Histone modifications of circulating nucleosomes are associated with changes in cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(42):e2404058121. doi:10.1073/pnas.2404058121
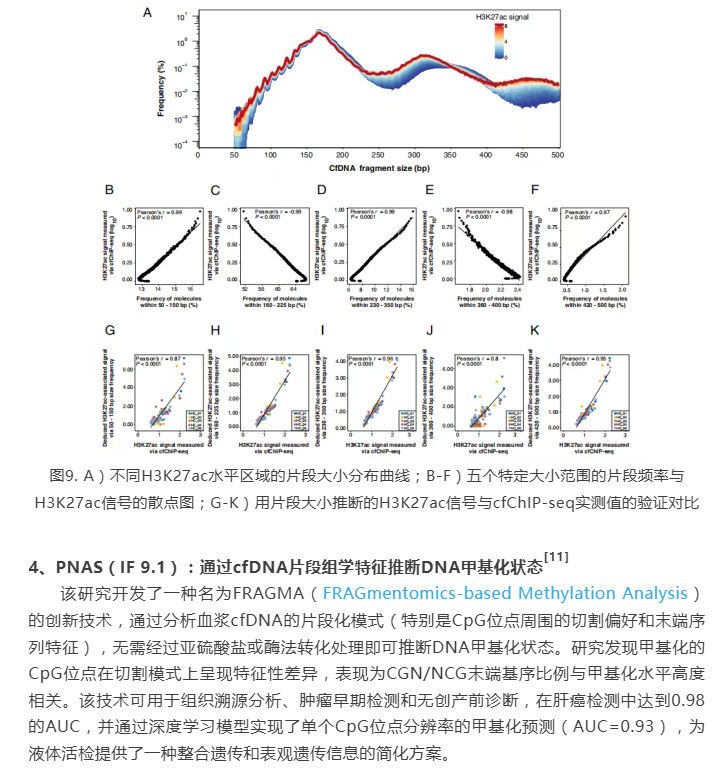
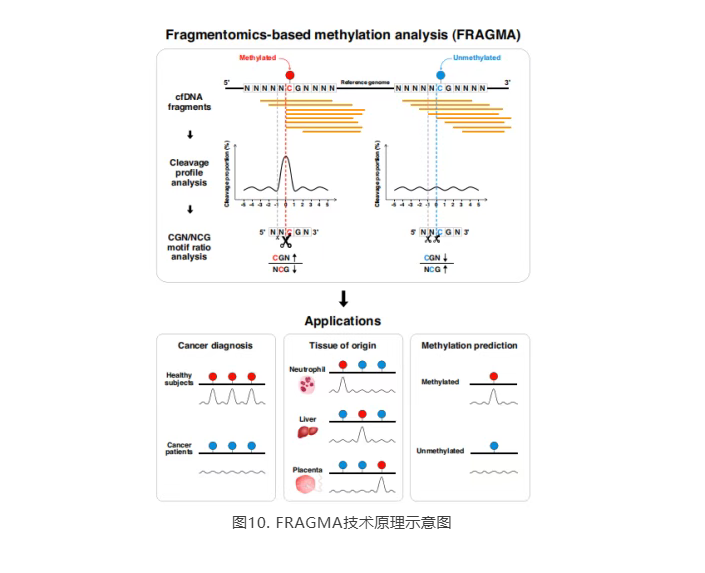
[11] Zhou Q, Kang G, Jiang P, et al. Epigenetic analysis of cell-free DNA by fragmentomic profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(44):e2209852119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2209852119
- - - 推荐阅读 - - -

cfChIP-seq:cfDNA/血浆游离核小体ChIP-seq测序服务
cfChIP-seq(cfDNA染色质免疫沉淀测序技术)是一种创新的液体活检技术,通过分析血浆中 cfDNA 的组蛋白修饰,为解析肿瘤细胞基因调控状态打开了全新窗口。
2025-06-25

cfDNA甲基化靶向测序EM-seq
基于酶学转化法的cfDNA甲基化靶向测序EM-seq,配合Twist靶向甲基化捕获探针,能够捕获和检测基因组中最新鉴定(包括UCSC、Ensembl、ENCODE等数据库)的生物学相关CpG甲基化区域,覆盖率达84.2%,中靶率高,优于传统亚硫酸氢盐测序法,是cfDNA液体活检甲基化疾病标志物的绝佳筛选工具。
2024-04-24
HEBER-seq—开启exRNA液体活检新时代
2021-12-06
