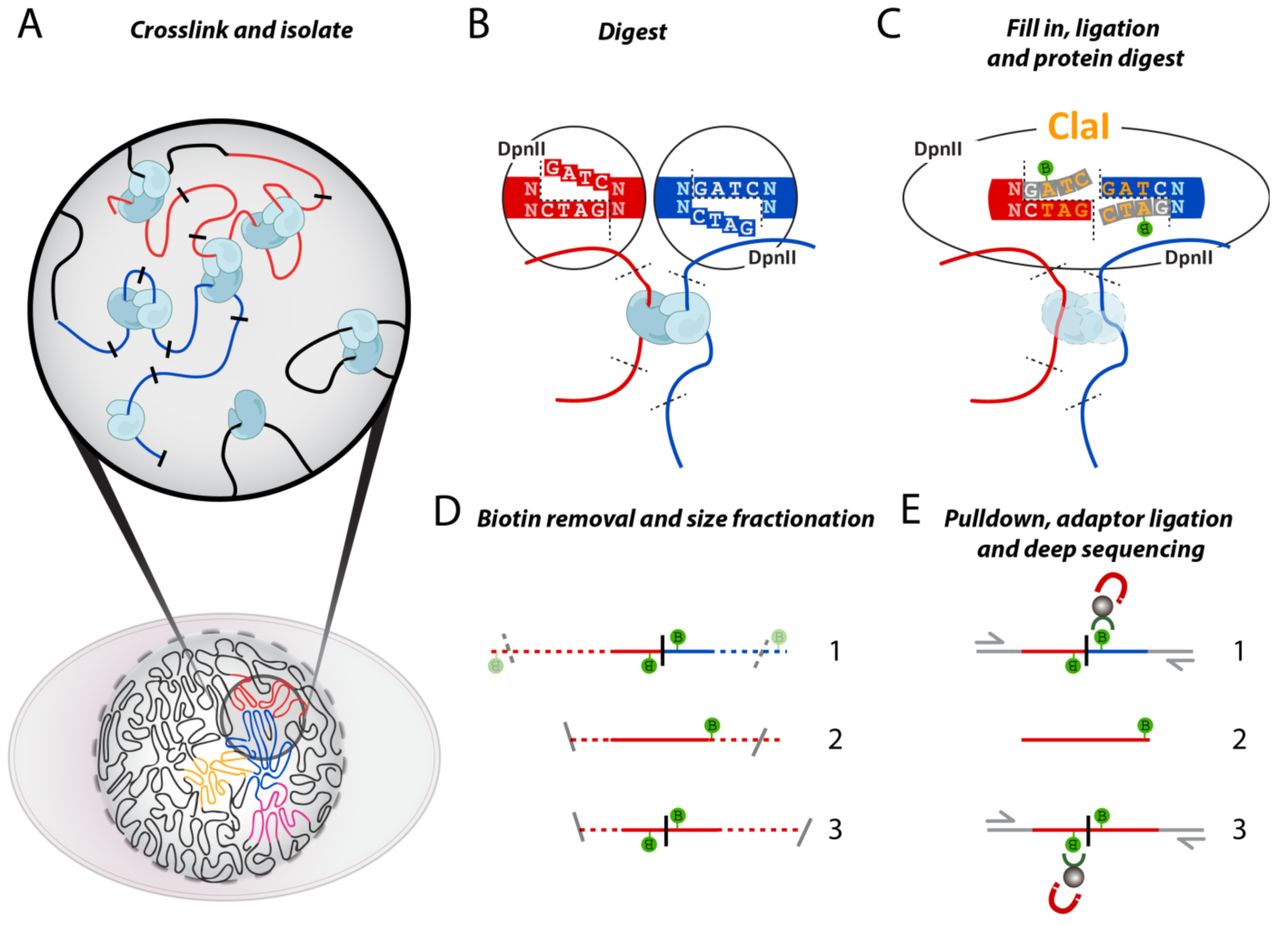
Hi-C(High-throughput Chromosome Conformation Capture)
Product Introduction
High-throughput Chromosome Conformation Capture (Hi-C) enables the study of DNA interactions across the entire genome, generating high-resolution 3D chromatin structure maps and providing information on three levels: A/B compartments, Topologically Associated Domains (TADs), and Chromatin Loops. As a pioneer in epigenetics research services in China, Epibiotek® can provide customers with a comprehensive research approach combining Hi-C and epigenetic multi-omics analysis, to conduct in-depth studies of the mechanisms underlying disease development from the perspective of 3D epigenomics.
Application
1.Investigate chromatin fragment–fragment interactions;
2.Construct three-dimensional genome-folding models;
3.Facilitate de novo or gap-closing genome assembly;
4.Integrate with RNA-seq to elucidate how 3D chromatin architecture modulates RNA expression;
5.Combine with ChIP-seq to dissect the interplay among regulatory elements, transcription factors, and chromatin interactions.
Sample Requirements
Fixed with formaldehyde crosslinking first.
≥100 mg/sample
Tissues
≥5×10⁶ cells/sample
Cells
Sample Species
Limited to human, mouse, and rat cells and tissues;other species require evaluation.
1. Data filtering
1.1 Raw data
1.2 Data filtering
1.3 Sequencing data quality distribution
1.4 Base distribution of sequencing data
2. Genomic alignment analysis
3. Alignment to restriction enzyme fragments
4. Proportion of Cis/Trans Interactions
5. Chromosome interactions
5.1 Inter-chromosomal interactions
5.2 Intra-chromosomal interactions
6. Structural analysis
6.1 A/B compartments
6.2 TAD calling
6.3 Identification and differential analysis of loops
6.4 3D modeling
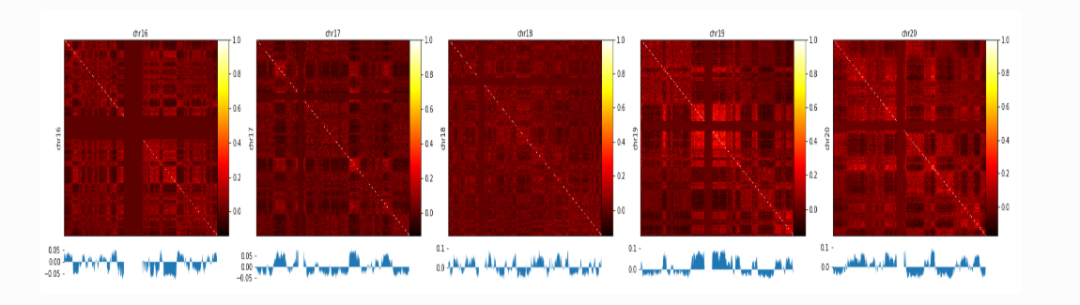
Figure 1. A/B compartment analysis
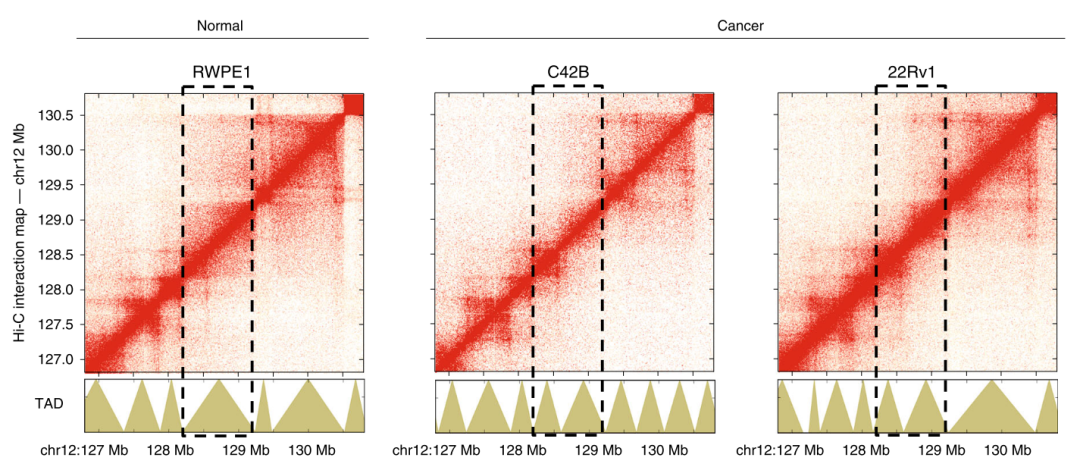
Figure 2. TAD identification
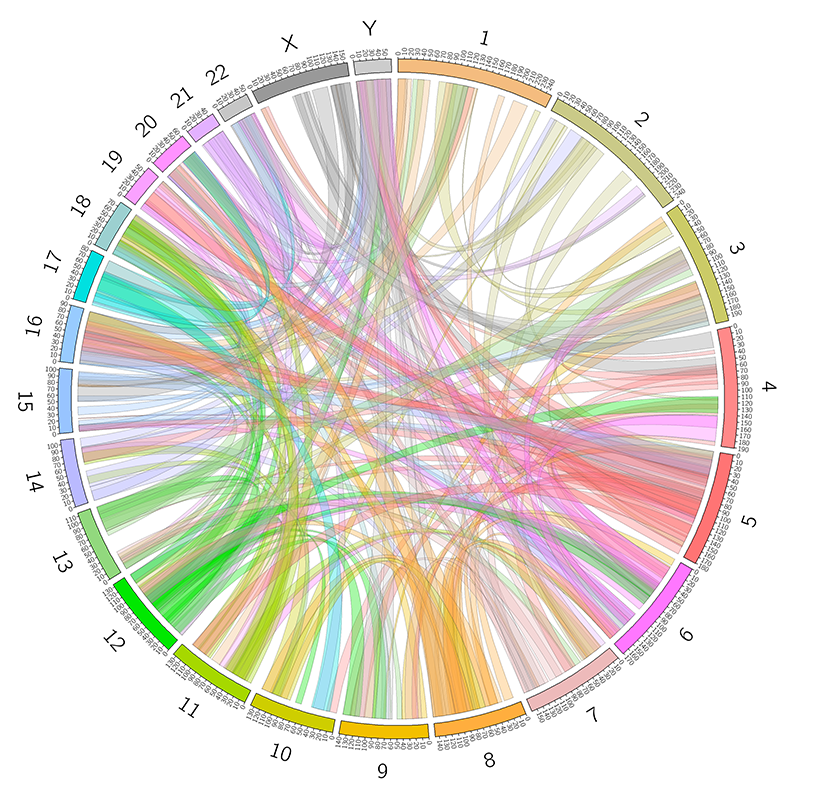
Figure 3. Loop identification
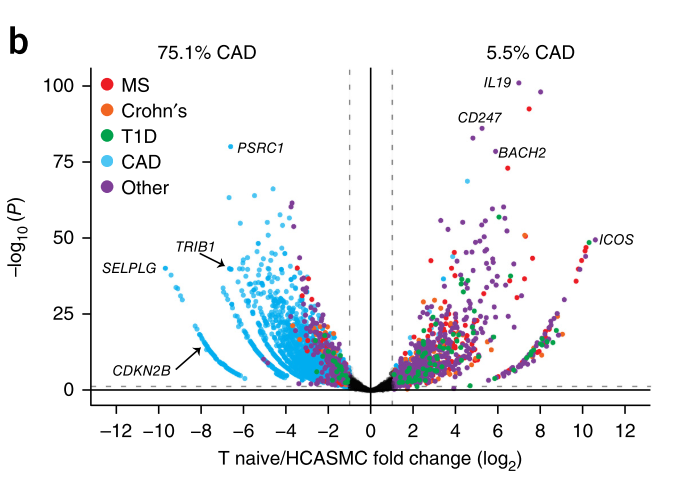
Figure 4. Loop difference analysis
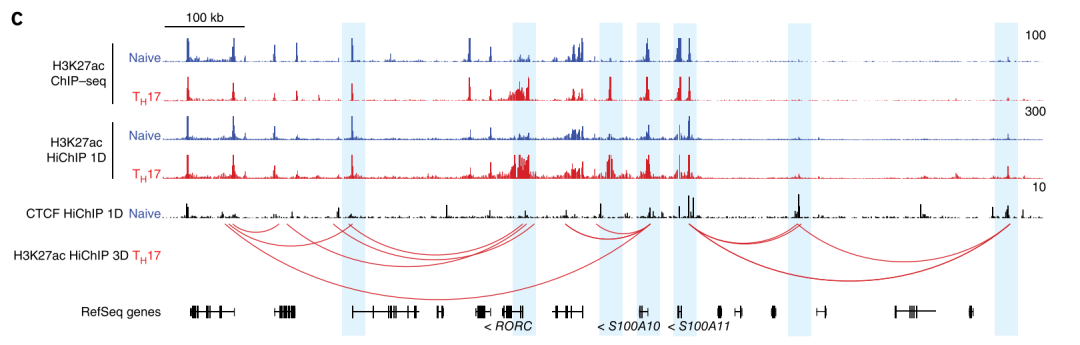
Figure 6. SNP and Loop association analysis (interested gene mapping)
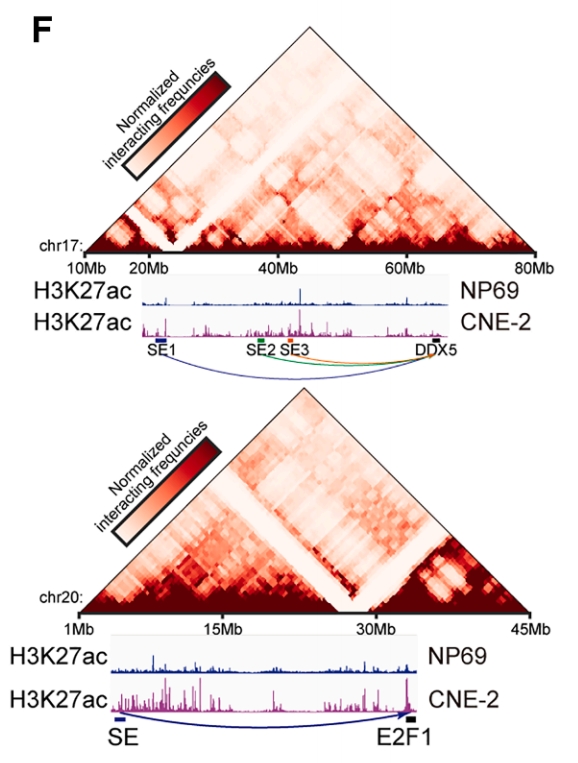
Figure 7. Long-range looping interactions of the SE regions with the TAD regions of DDX5 and E2F1 in CNE2 cells, identified using Hi-C analysis, and the H3K27ac ChIP signals of CNE2 and NP69.
Customer Articles
《Cell Rep Med》DDX5 super-enhancer promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by enhancing ADAM10 transcription
This study unveils a crucial mechanism of resistance to anti-angiogenic drugs (AADs)—compensatory formation of vascular mimicry (VM). The research team employed DIA mass spectrometry-based proteomics to identify ADAM10 as a key protein promoting VM formation, which was found to be significantly enriched in exosomes from metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Through CUT&Tag sequencing analysis of H3K27ac modifications to identify super-enhancers, combined with Hi-C technology to decipher the three-dimensional genomic architecture, it was discovered that two transcription factors, DDX5 and E2F1, are activated by super-enhancers via long-range chromatin looping interactions, subsequently upregulating ADAM10 expression. In vivoand in vitroexperiments confirmed that the combination of IM (a specific inhibitor, context-dependent) and nimotuzumab simultaneously inhibited both angiogenesis and VM formation, effectively overcoming AAD resistance, suppressing nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis, and improving prognosis. This research provides a novel epigenetic perspective for understanding the mechanisms of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy and suggests a potential combination treatment strategy. (CUT&Tag and Hi-C services were provided by Epibiotek)
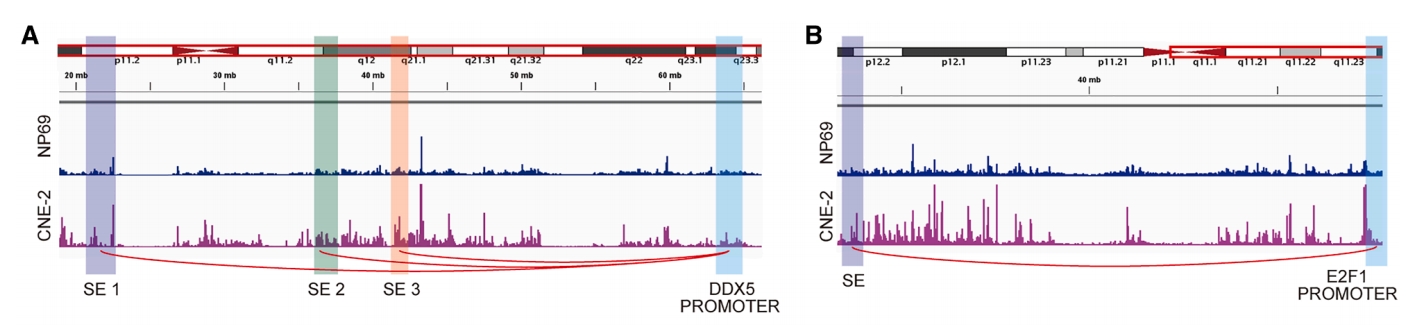
Figure 8. The chromatin long-range looping interactions between SE regions and promoters of DDX5 (A) and E2F1 (B).
